本节引言:
Drawable资源使用注意事项
好的,要注意的地方大概就这些,下面我们来对Android中给我们提供的13种Drawable进行学习!
1.ColorDrawable
1).Java中定义ColorDrawable:
ColorDrawable drawable = new ColorDrawable(0xffff2200); txtShow.setBackground(drawable);
2).在xml中定义ColorDrawable:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<color
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:color="#FF0000"/>
当然上面这些用法,其实用得不多,更多的时候我们是在res/values目录下创建一个color.xml 文件,然后把要用到的颜色值写到里面,需要的时候通过@color获得相应的值,比如:
3).建立一个color.xml文件
比如:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<color name="material_grey_100">#fff5f5f5</color>
<color name="material_grey_300">#ffe0e0e0</color>
<color name="material_grey_50">#fffafafa</color>
<color name="material_grey_600">#ff757575</color>
<color name="material_grey_800">#ff424242</color>
<color name="material_grey_850">#ff303030</color>
<color name="material_grey_900">#ff212121</color>
</resources>
然后如果是在xml文件中话我们可以通过@color/xxx获得对应的color值 如果是在Java中:
int mycolor = getResources().getColor(R.color.mycolor); btn.setBackgroundColor(mycolor);
ps:另外有一点要注意,如果我们在Java中直接定义颜色值的话,要加上0x,而且不能把透明度漏掉:
int mycolor = 0xff123456; btn.setBackgroundColor(mycolor);
4).使用系统定义好的color:
比如:BLACK(黑色),BLUE(蓝色),CYAN(青色),GRAY(灰色),GREEN(绿色),RED(红色),WRITE(白色),YELLOW(黄色)! 用法: btn.setBackgroundColor(Color.BLUE); 也可以获得系统颜色再设置:
int getcolor = Resources.getSystem().getColor(android.R.color.holo_green_light); btn.setBackgroundColor(getcolor);
xml中使用:android:background="@android:color/black"
5).利用静态方法argb来设置颜色:
2.NiewPatchDrawable
接着介绍两个没什么卵用的东东:
xml定义NinePatchDrawable:
<!--pic9.xml-->
<!--参数依次为:引用的.9图片,是否对位图进行抖动处理-->
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<nine-patch
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:src="@drawable/dule_pic"
android:dither="true"/>
使用Bitmap包装.9图片:
<!--pic9.xml-->
<!--参数依次为:引用的.9图片,是否对位图进行抖动处理-->
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<bitmap
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:src="@drawable/dule_pic"
android:dither="true"/>
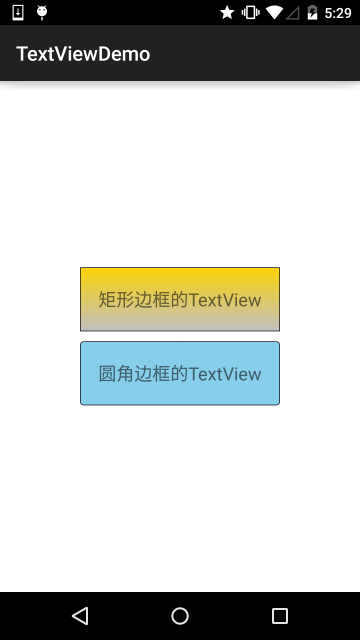
3.ShapeDrawable
使用示例: 2.3.1 TextView(文本框)详解
4.GradientDrawable
代码示例:(三种渐变效果的演示):
运行效果图:

先在drawable下创建三个渐变xml文件:
(线性渐变)gradient_linear.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<shape
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:shape="oval" >
<gradient
android:angle="90"
android:centerColor="#FFEB82"
android:endColor="#35B2DE"
android:startColor="#DEACAB" />
<stroke
android:dashGap="5dip"
android:dashWidth="4dip"
android:width="3dip"
android:color="#fff" />
</shape>
(发散渐变)gradient_radial.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:innerRadius="0dip"
android:shape="ring"
android:thickness="70dip"
android:useLevel="false" >
<gradient
android:centerColor="#FFEB82"
android:endColor="#35B2DE"
android:gradientRadius="70"
android:startColor="#DEACAB"
android:type="radial"
android:useLevel="false" />
</shape>
(平铺渐变)gradient_sweep.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:innerRadiusRatio="8"
android:shape="ring"
android:thicknessRatio="3"
android:useLevel="false" >
<gradient
android:centerColor="#FFEB82"
android:endColor="#35B2DE"
android:startColor="#DEACAB"
android:type="sweep"
android:useLevel="false" />
</shape>
调用三个drawable的activity_main.xml:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txtShow1"
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:background="@drawable/gradient_linear" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txtShow2"
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:background="@drawable/gradient_radial" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txtShow3"
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:background="@drawable/gradient_sweep" />
</LinearLayout>
好的,就是那么简单~当然,如果想绘制更加复杂的图形的话,只用xml文件不远远不足的, 更复杂的效果则需要通过Java代码来完成,下面演示的是摘自网上的一个源码:
运行效果图:
实现代码:
MainActivity.java:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(new SampleView(this));
}
private static class SampleView extends View {
private ShapeDrawable[] mDrawables;
private static Shader makeSweep() {
return new SweepGradient(150, 25,
new int[] { 0xFFFF0000, 0xFF00FF00, 0xFF0000FF, 0xFFFF0000 },
null);
}
private static Shader makeLinear() {
return new LinearGradient(0, 0, 50, 50,
new int[] { 0xFFFF0000, 0xFF00FF00, 0xFF0000FF },
null, Shader.TileMode.MIRROR);
}
private static Shader makeTiling() {
int[] pixels = new int[] { 0xFFFF0000, 0xFF00FF00, 0xFF0000FF, 0};
Bitmap bm = Bitmap.createBitmap(pixels, 2, 2,
Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888);
return new BitmapShader(bm, Shader.TileMode.REPEAT,
Shader.TileMode.REPEAT);
}
private static class MyShapeDrawable extends ShapeDrawable {
private Paint mStrokePaint = new Paint(Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
public MyShapeDrawable(Shape s) {
super(s);
mStrokePaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
}
public Paint getStrokePaint() {
return mStrokePaint;
}
@Override protected void onDraw(Shape s, Canvas c, Paint p) {
s.draw(c, p);
s.draw(c, mStrokePaint);
}
}
public SampleView(Context context) {
super(context);
setFocusable(true);
float[] outerR = new float[] { 12, 12, 12, 12, 0, 0, 0, 0 };
RectF inset = new RectF(6, 6, 6, 6);
float[] innerR = new float[] { 12, 12, 0, 0, 12, 12, 0, 0 };
Path path = new Path();
path.moveTo(50, 0);
path.lineTo(0, 50);
path.lineTo(50, 100);
path.lineTo(100, 50);
path.close();
mDrawables = new ShapeDrawable[7];
mDrawables[0] = new ShapeDrawable(new RectShape());
mDrawables[1] = new ShapeDrawable(new OvalShape());
mDrawables[2] = new ShapeDrawable(new RoundRectShape(outerR, null,
null));
mDrawables[3] = new ShapeDrawable(new RoundRectShape(outerR, inset,
null));
mDrawables[4] = new ShapeDrawable(new RoundRectShape(outerR, inset,
innerR));
mDrawables[5] = new ShapeDrawable(new PathShape(path, 100, 100));
mDrawables[6] = new MyShapeDrawable(new ArcShape(45, -270));
mDrawables[0].getPaint().setColor(0xFFFF0000);
mDrawables[1].getPaint().setColor(0xFF00FF00);
mDrawables[2].getPaint().setColor(0xFF0000FF);
mDrawables[3].getPaint().setShader(makeSweep());
mDrawables[4].getPaint().setShader(makeLinear());
mDrawables[5].getPaint().setShader(makeTiling());
mDrawables[6].getPaint().setColor(0x88FF8844);
PathEffect pe = new DiscretePathEffect(10, 4);
PathEffect pe2 = new CornerPathEffect(4);
mDrawables[3].getPaint().setPathEffect(
new ComposePathEffect(pe2, pe));
MyShapeDrawable msd = (MyShapeDrawable)mDrawables[6];
msd.getStrokePaint().setStrokeWidth(4);
}
@Override protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
int x = 10;
int y = 10;
int width = 400;
int height = 100;
for (Drawable dr : mDrawables) {
dr.setBounds(x, y, x + width, y + height);
dr.draw(canvas);
y += height + 5;
}
}
}
}




